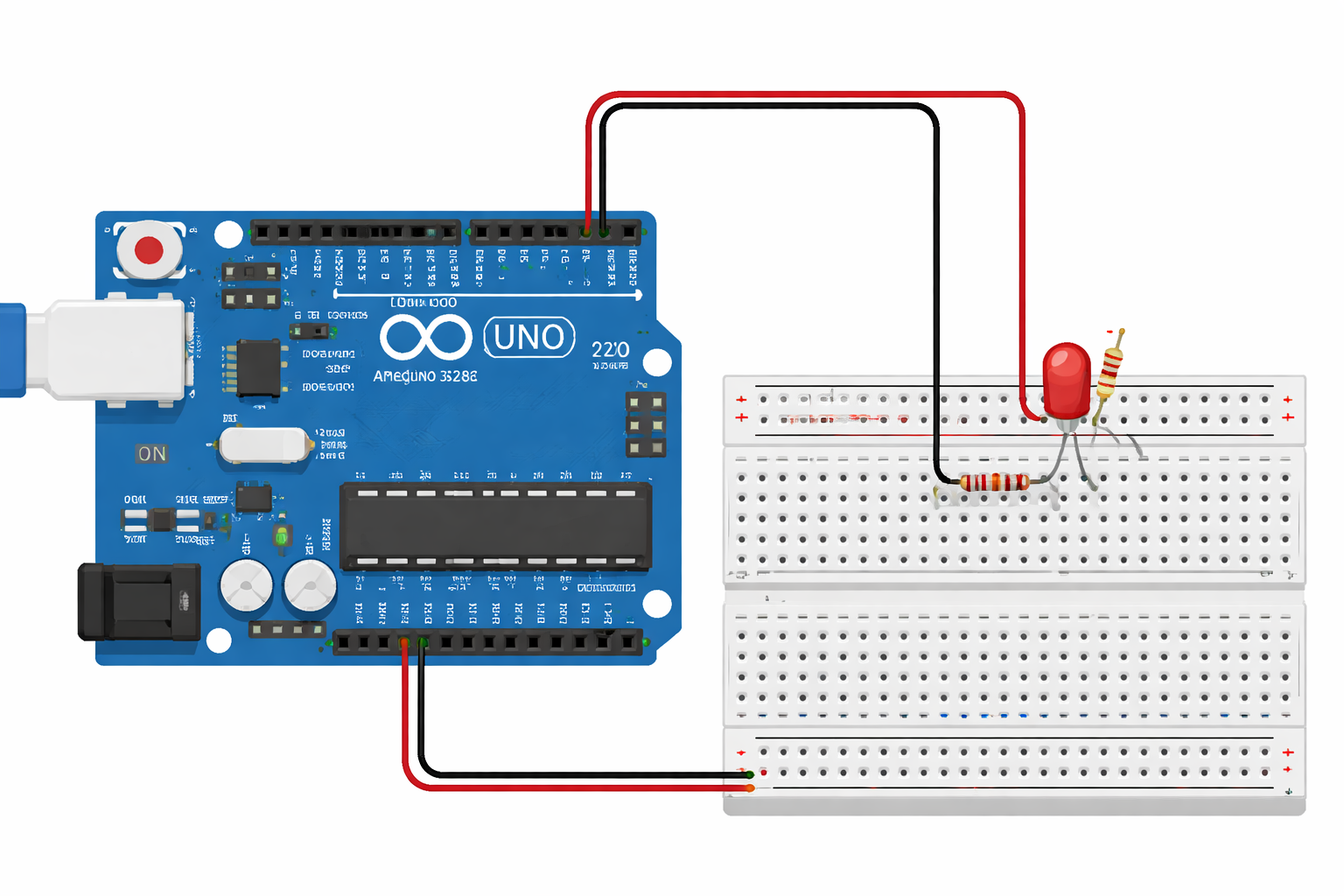
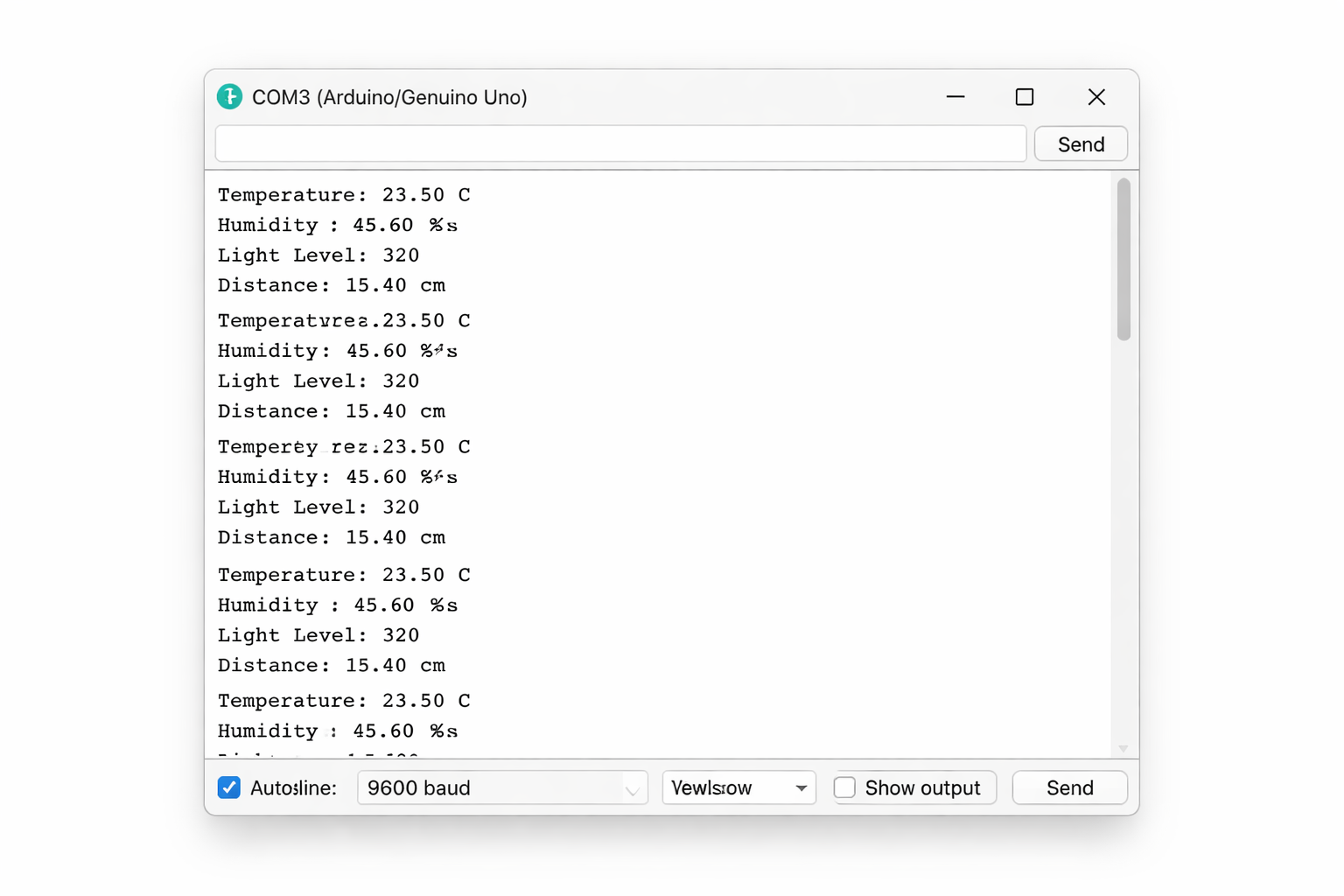
Imagine This...
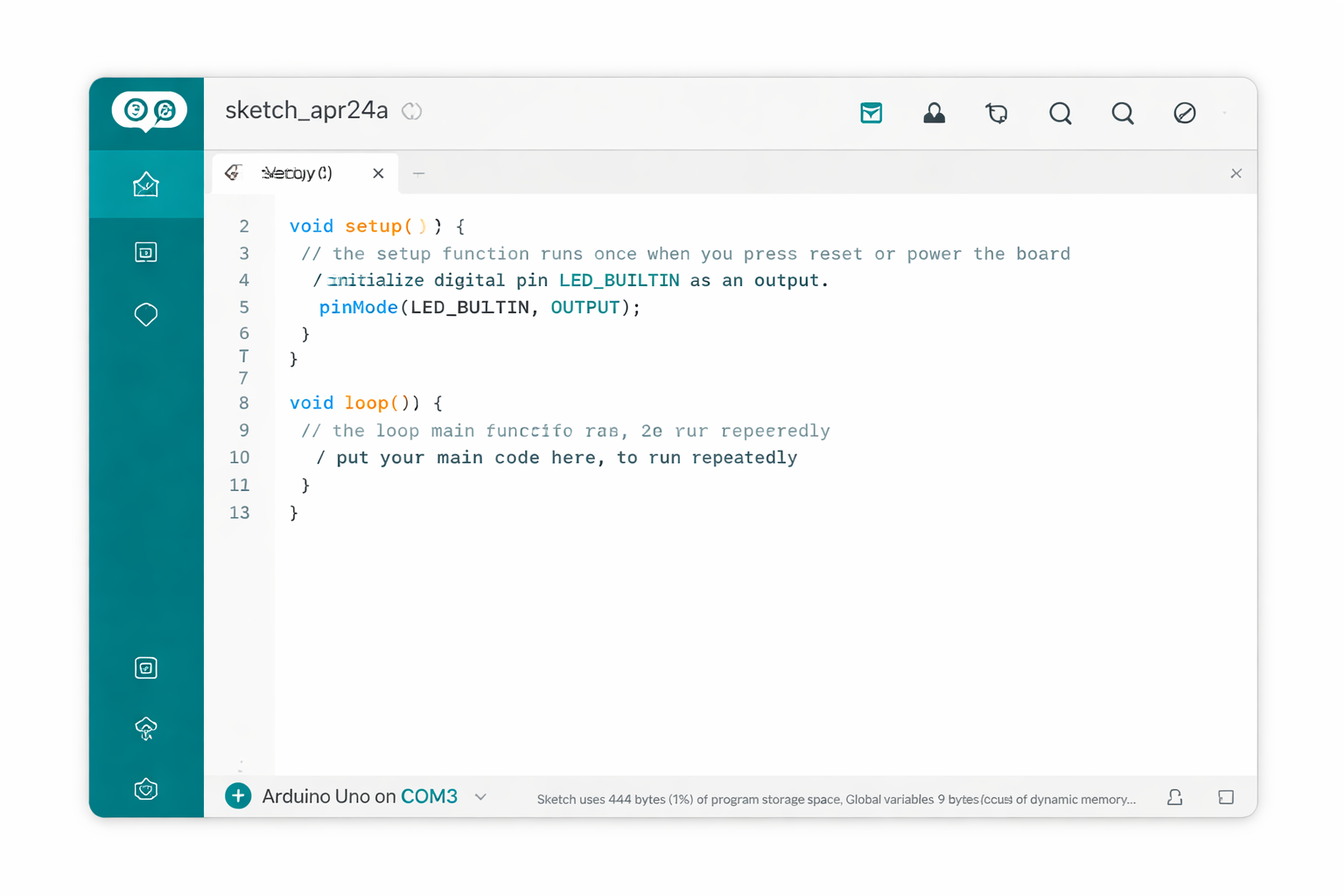
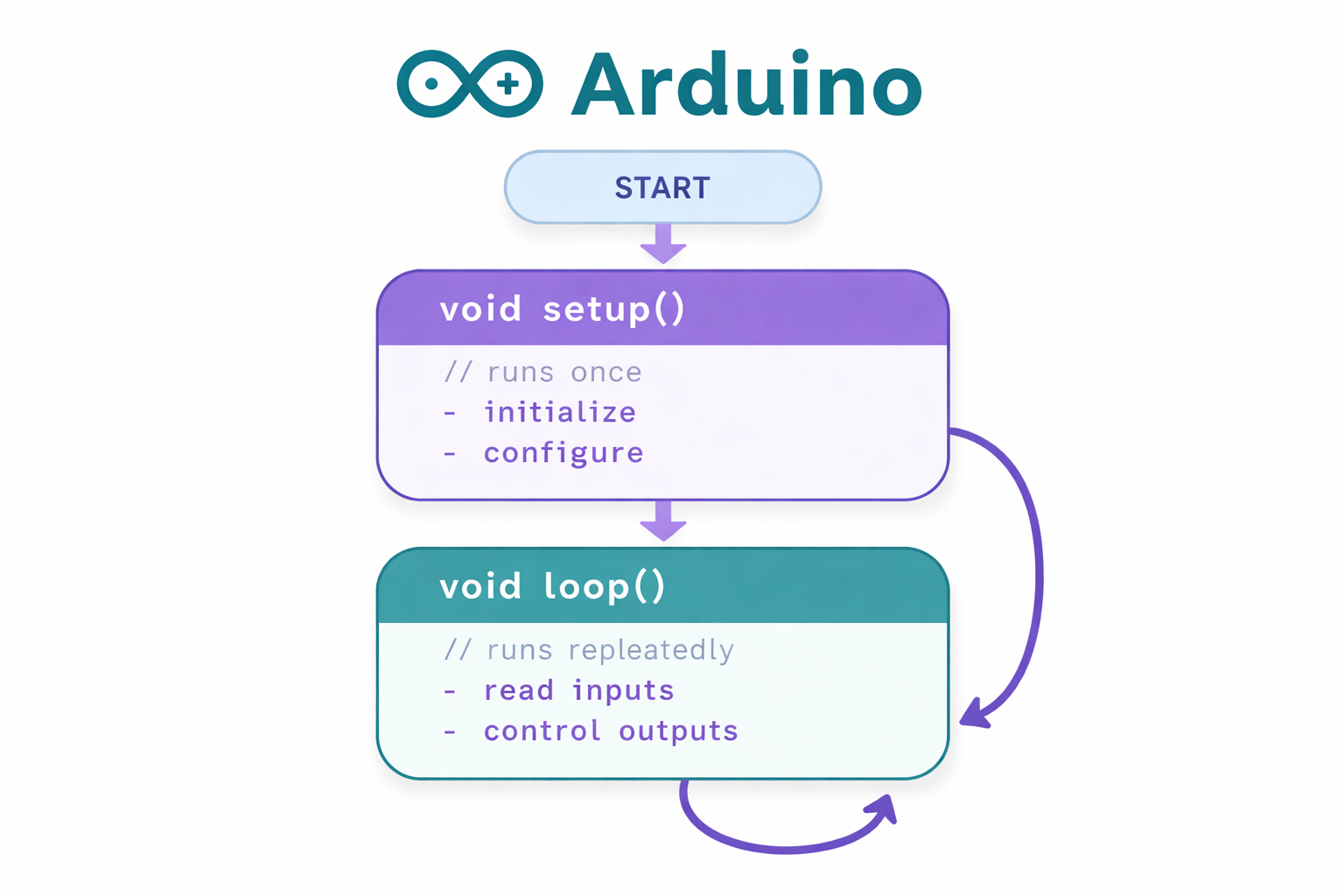
In less time than it takes to make coffee, you could write 10 lines of code that makes an LED blink. That's the power of Arduino - a tiny computer that turns your ideas into reality.
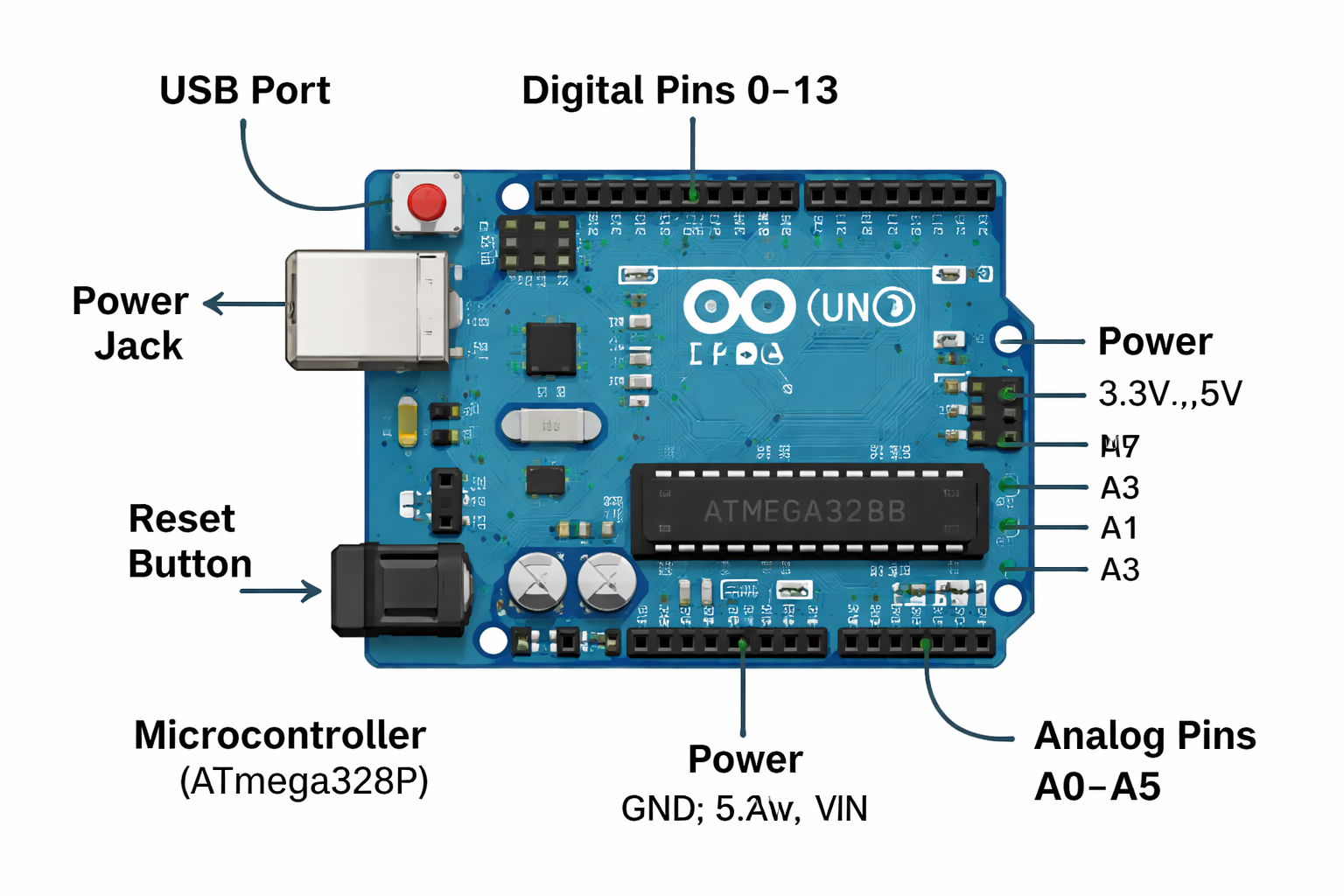
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform that lets beginners and experts alike build interactive projects. From blinking lights to robots, smart homes to weather stations, Arduino is the foundation for millions of maker projects worldwide.
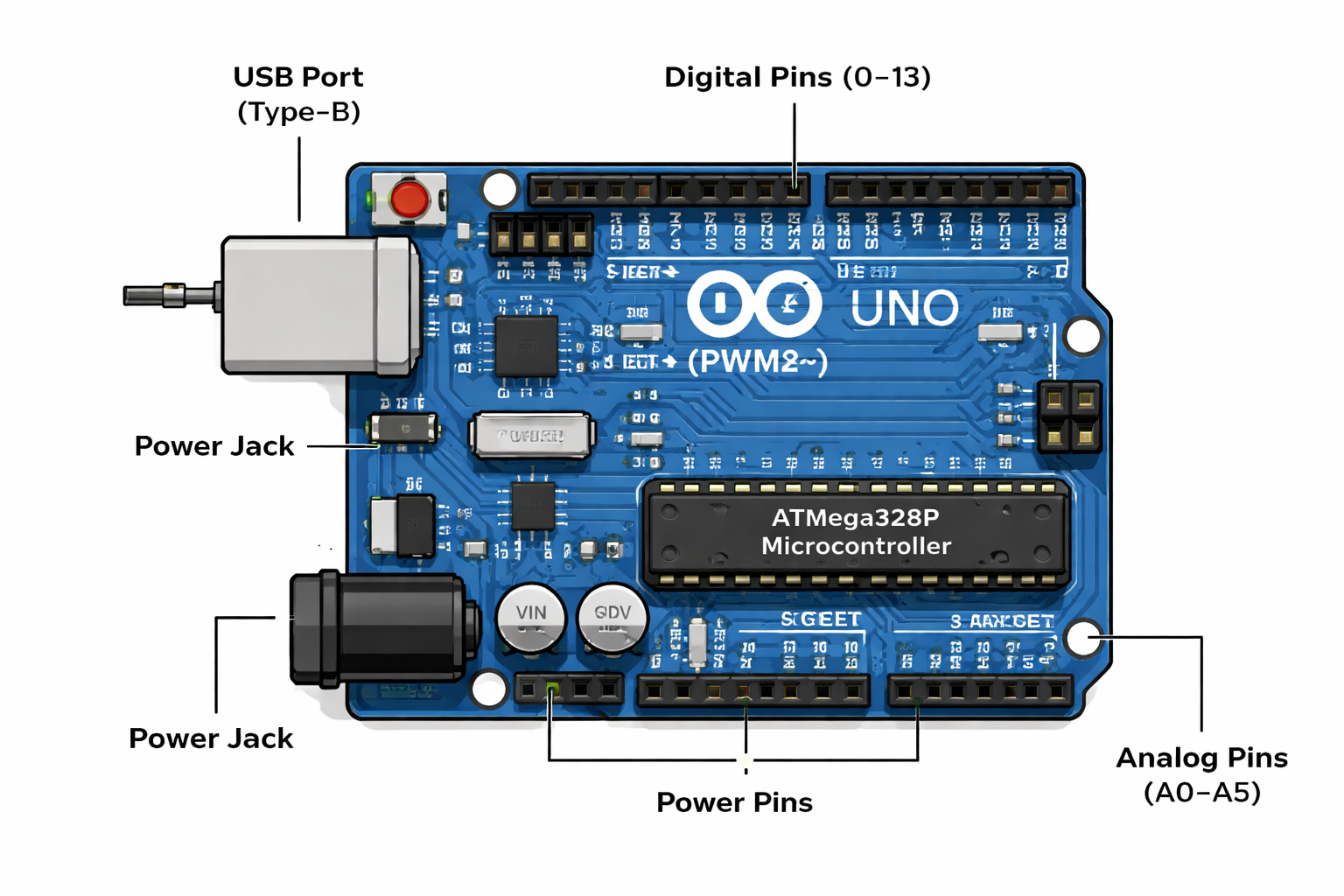
What's in this lesson: Hardware components, programming basics, your first circuit, and assessment.
Why this matters: Arduino skills open doors to robotics, IoT, automation, and physical computing careers.